Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Manufacturing Plant, Construction works , Energy & Mining
Weight (KG)
3000
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components
Not Available
Core Components
Gear, Ring Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1year
Shape
Ring Gear
Standard or Nonstandard
Nonstandard
Tooth Profile
Helical Gear,spur gear
Material
Steel
Processing
Forging
Pressure Angle
custom
Brand Name
TS
Product Name
Large Ring Gear
Module No.
5-180
Process
Milling,hobbing
Surface treatment
as request
Heat treatment
Q&T
Application
Industry machinery,transmission equipment
Standard
DIN ANSI ISO
Certificate
ISO
OEM Service
YES
Delivery time
15-60days
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package adapting to CHINAMFG transport
Port
ZheJiang ,HangZhou
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
5 Piece/Pieces per Month
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses.
Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula:
η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100%
Where:
η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage.
Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system.
Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system.
Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the gear affects the efficiency. Well-designed gear teeth with accurate involute profiles can minimize friction and power losses during meshing.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication between the gear teeth reduces friction, wear, and heat generation, improving gear efficiency. Insufficient or inadequate lubrication can result in increased power losses and reduced efficiency.
- Gear Material: The selection of gear material affects efficiency. Materials with low friction coefficients and good wear resistance can help minimize power losses. Higher-quality materials and specialized gear coatings can improve efficiency.
- Gear Alignment and Meshing: Proper alignment and precise meshing of the gear teeth are essential for optimal efficiency. Misalignment or incorrect gear meshing can lead to increased friction, noise, and power losses.
- Bearing Friction: The efficiency of a gear system is influenced by the friction in the bearings supporting the gear shafts. High-quality bearings with low friction characteristics can contribute to improved gear efficiency.
- Load Distribution: Uneven load distribution across the gear teeth can result in localized power losses and reduced efficiency. Proper design and gear system configuration should ensure even load distribution.
Interpreting Gear Efficiency:
The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation.
It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices.
By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.

Are spur gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Spur gears are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including those involving high-torque requirements. However, their suitability for high-torque applications depends on various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are designed to transmit power and torque between parallel shafts. They have straight teeth that engage fully, providing efficient power transfer. The suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications can be evaluated based on the following considerations:
- Load Distribution: Spur gears distribute the transmitted load over a larger contact area compared to other gear types. This characteristic allows them to handle higher torque loads effectively.
- Size and Diameter: The size and diameter of the spur gears play a crucial role in their ability to handle high torque. Larger gear diameters provide increased torque capacity due to the longer lever arm and larger contact area between the gear teeth.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for the spur gears is essential for high-torque applications. Strong and durable materials, such as hardened steel or alloy steels, are commonly used to ensure the gears can withstand the high stresses and torque loads without deformation or failure.
- Gear Design: Proper gear design considerations, such as tooth profile, module or pitch, and the number of teeth, can impact the torque-carrying capacity of spur gears. Design parameters should be optimized to ensure sufficient tooth strength and minimize the risk of tooth breakage or excessive wear.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Adequate lubrication is critical for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in high-torque spur gear applications. Regular maintenance, including lubricant replacement and gear inspections, can help identify and address any issues that may affect the gear’s torque-handling capabilities.
- Supporting Components: The overall system design, including the selection of bearings, shafts, and housing, should be considered to ensure proper support and alignment of the spur gears. Well-designed supporting components contribute to the overall torque capacity of the system.
While spur gears can handle high torque, it’s important to note that there are limitations to their torque capacity. Factors such as gear size, material strength, tooth design, and operating conditions can affect the maximum torque the gears can safely transmit without failure.
In some cases, other gear types such as helical gears or bevel gears may be more suitable for specific high-torque applications. These gears offer advantages such as increased load-carrying capacity, improved torque transfer efficiency, and reduced noise and vibration levels.
Ultimately, the suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications should be evaluated based on the specific requirements, operating conditions, and industry standards applicable to the particular application.
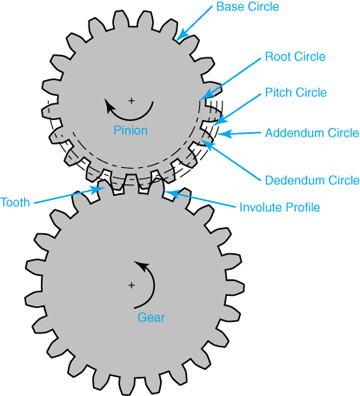
How do spur gears contribute to power transmission?
Spur gears play a crucial role in power transmission due to their specific design and tooth engagement. Here’s a detailed explanation of how spur gears contribute to power transmission:
- Direct Tooth Engagement: Spur gears have straight teeth that mesh directly with each other. This direct tooth engagement ensures efficient transfer of power from one gear to another. As the driving gear rotates, its teeth come into contact with the teeth of the driven gear, enabling the transfer of rotational motion and torque.
- Uniform Load Distribution: The teeth of spur gears distribute the transmitted load evenly across the gear surfaces. The straight, parallel teeth provide a larger contact area compared to other gear types, resulting in improved load-carrying capacity and reduced stress concentration. This uniform load distribution helps prevent premature wear and failure of the gears, ensuring reliable power transmission.
- Efficiency: Spur gears are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The direct tooth engagement and parallel shaft arrangement minimize energy losses during rotation. The teeth mesh smoothly, resulting in minimal friction and reduced power dissipation. This efficiency is beneficial in applications where maximizing power transfer and minimizing energy waste are crucial.
- Speed and Torque Conversion: Spur gears allow for speed and torque conversion between the driving and driven shafts. By using gears with different numbers of teeth, the rotational speed and torque can be adjusted to match the requirements of the application. For example, a small gear driving a larger gear will result in a higher torque output at a lower speed, while a larger gear driving a smaller gear will result in a higher speed output at a lower torque.
- Directional Control: The arrangement of spur gears can be used to control the rotational direction of the driven shaft relative to the driving shaft. By meshing gears with opposite orientations (e.g., one gear with clockwise teeth and another gear with counterclockwise teeth), the direction of rotation can be reversed. This directional control is essential in applications where the desired motion needs to be reversed or changed.
- Multiple Gear Configurations: Spur gears can be combined in various configurations to form gear trains, allowing for complex power transmission systems. Gear trains consist of multiple gears meshing together, with each gear contributing to the overall power transmission. Gear trains can alter speed, torque, and direction, providing flexibility in adapting power transmission to specific requirements.
- Compatibility with Other Components: Spur gears are compatible with a wide range of other mechanical components, such as shafts, bearings, and housings. This compatibility allows for easy integration into different systems and machinery. Spur gears can be mounted on shafts using keyways, set screws, or other mounting methods, ensuring secure and reliable power transmission.
Overall, spur gears are essential in power transmission systems due to their direct tooth engagement, uniform load distribution, high efficiency, speed and torque conversion capabilities, directional control, compatibility with other components, and the ability to form complex gear trains. These characteristics make spur gears a versatile and widely used choice for transmitting power in various applications across industries.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06